– COP28, Bonn Climate Conference…. Global collective efforts for climate change are rapidly gaining traction.
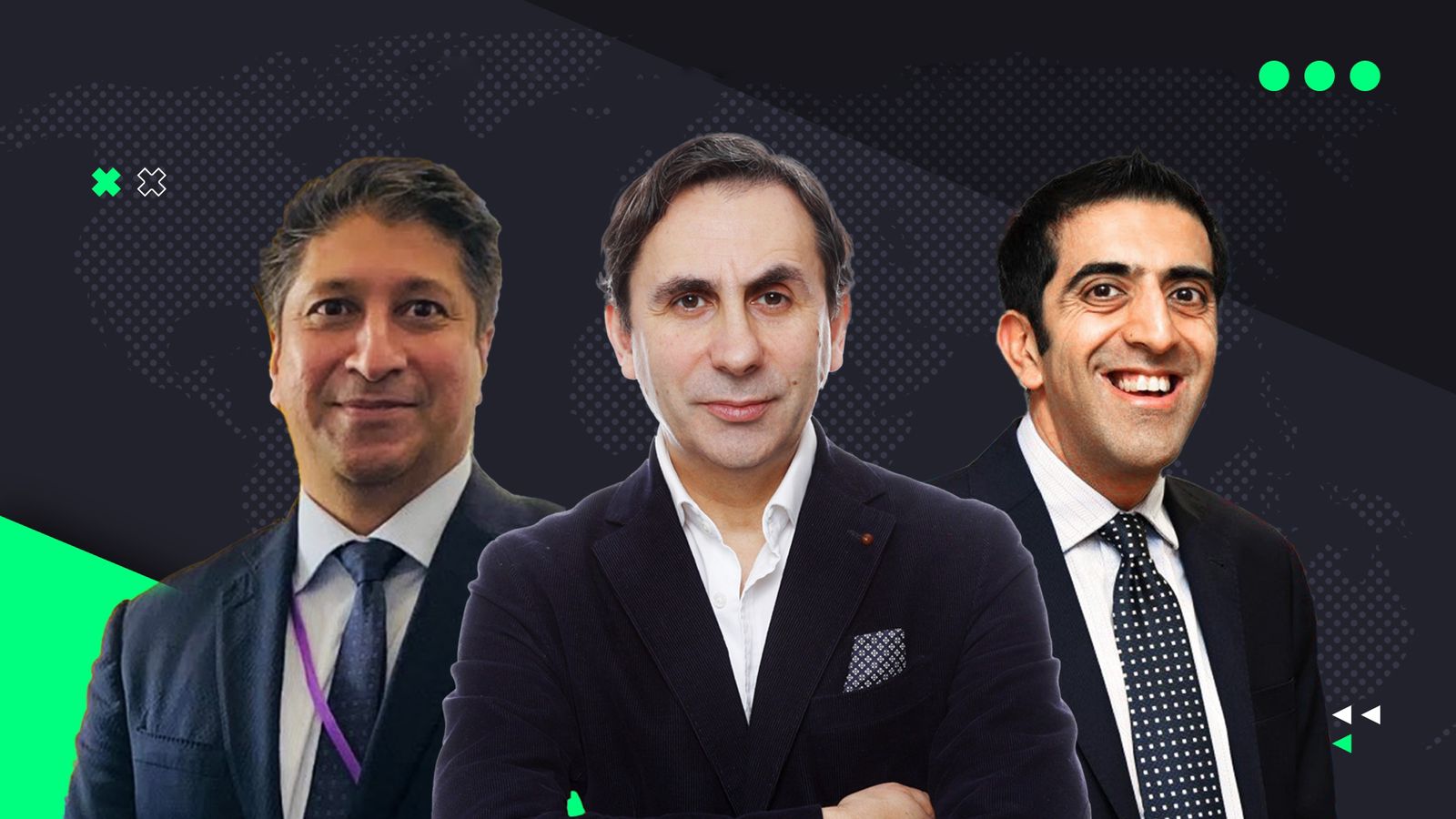
– Dinis Guarda interviews Hirander Misra, CEO of ZERO13 which is a marketplace aggregation solution for carbon credits as well as ESG real-world assets, and Asad Sultan, CEO of Verdana and its subsidiary EcoConsortium, Asia-Pacific’s first digital carbon registry.
– The experts discuss the urgent need for end-to-end digital connectivity in the carbon eco-system for transparency, efficiency and scalability.
Global average temperatures have already risen to 1.1 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels resulting in more frequent and intense extreme weather events worldwide. An Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report brings into sharp focus some of the present implications of climate change and also some of the projected effects in the future.
The urgency to combat climate change and promote sustainable practices has given rise to a global focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles. As organisations and governments strive to achieve Net Zero emissions, a powerful tool emerges: the digital interconnection of ESG markets.
Digitally interconnecting ESG markets involves leveraging technology to create seamless and efficient communication channels between various stakeholders. Interconnecting data, platforms, and standards, enables enhanced collaboration, transparency, and accountability, accelerating progress towards Net Zero goals.
ZERO 13, an initiative by GMEX Group, is digitally interconnecting ESG markets to achieve Net Zero targets. This is helping to achieve Net Zero by combining AI and blockchain to restore trust in carbon credit markets, addressing greenwashing, double counting, price transparency, vertical silos and market fragmentation.
Hirander Misra is Chairman & CEO of GMEX Group, a company that offers innovative solutions for the creation & operation of electronic exchanges and post-trading services and the CEO of ZERO13, part of the GMEX Group and a regulated digital exchange (SECDEX) and marketplace aggregation solution for carbon credits as well as ESG real-world assets.
“There are many projects contributing to the ecosystem in parts, but no one is providing a comprehensive solution. The market, on the other hand, needs a solution that is packaged for them and covers the whole vertical value chain. That is why ZERO13 has been launched”, highlighted Hirander.
By connecting to Verdana and EcoConsortium, Zero13 offers turn-key digitalisation across the carbon marketplace vertical.
EcoConsortium is a carbon registry that maintains project details and carbon credit related records digitally, on behalf of standards bodies. EcoConsortium facilitates carbon credit transactions by connecting projects over a digital measurement, reporting, and verification (dMRV) platform to project validators & verifiers appointed on behalf of the standards bodies, as well as to carbon exchanges to facilitate sales of certified carbon credits.
Commenting on the need for digital interconnection, Asad Sultan said:
“The current carbon market volume is estimated to be around $12 billion, and is expected to reach about $30 billion in the next 5-6 years. That’s a fairly strong growth rate. Anyone playing in this segment is in a big marketplace. Therefore, the solutions that they are targeting to address are going to be very valuable.
We recognise that if we bring our expertise to the table, i.e., digital measurement, reporting, and verification, and combine it with others like ZERO13, we can bring in some value to the fragmented efforts around the globe and create an impact.”
More interviews
ZERO13 leverages digital interconnection for enhanced ESG markets

Digital interconnection serves as a catalyst for transformative advancements in ESG markets, delivering significant benefits across multiple dimensions.
By seamlessly integrating data, it ensures consistent and standardised reporting, facilitating transparency and trust among investors, regulators, and organisations. This enhanced data integration empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, conduct thorough risk assessments, and encourage responsible investments aligned with ESG principles.
“Provenance is very important. With the technologies that we have today: AI, blockchain, IoT, there’s much more ability to measure many parameters accurately and show the end-to-end process transparently to the consumer”, said Hirander.
Digital interconnection enables accurate and comprehensive impact measurement and reporting, revolutionising the evaluation of ESG initiatives. By amalgamating data from diverse sources such as environmental sensors, supply chain records, and social impact indicators, stakeholders gain a holistic understanding of the true impact of their sustainability efforts. This empowers organisations to track progress, identify improvement areas, and demonstrate their contributions towards achieving ambitious Net Zero targets.
The interconnection of ESG markets through digital platforms establishes a dynamic ecosystem that enhances market efficiency and liquidity.
“Simply reporting the emissions isn’t enough. It does help optimize your energy consumption and reduce emission footprint. But, in order to monetise the efficiencies that you are bringing into your process, you also need to go midstream and downstream and connect digitally with certification bodies on one hand and markets & exchanges on the other. Such end-to-end digitization is in fact, a game changing idea”, Asad highlighted.
By leveraging interconnected systems, investors gain access to a broader range of sustainable investment opportunities, enabling easier allocation of capital towards environmentally and socially responsible projects. Asad further added:
“By focusing on multiple marketplaces that are siloed, we are able to scale out and make a solution accessible to as many number of players, thereby encouraging more market participants, both users and developers.”
The reduction of barriers to entry, coupled with increased innovation, attracts a wider pool of investors, fuelling the transition towards a resilient and low-carbon economy.
ZERO13: An initiative for enabling standardisation and global compatibility
Digitalisation and interconnected efforts enable the standardisation and compatibility of carbon credit and carbon financing processes. Explaining the mechanics of an interoperable platform, Hirander said:
“Once the process is digitised and the inventory is part of the construct with ZERO13, you can distribute your credits all over the world and tap into the demand in the distribution curve in any part of the world.
ZERO13 also facilitates transactions across the blockchains, uses APIs to plug-in some analogue players, and facilitates transactions across borders and geo-political boundaries. When you bring all these aspects together, it creates a kind of network effect which helps to grow the market together.”
By establishing common frameworks, protocols, and data formats, interoperability is achieved, allowing seamless integration and exchange of information between different carbon credit registries, trading platforms, and financial institutions.
“With the interoperability that a platform like ZERO13 offers, we can match the fragmented groups across the world together so that the producers of carbon credits, and also the users, can offset themselves through their nationally determined targets”, Asad highlighted.
This standardisation reduces complexity, enhances market liquidity, and facilitates the scaling up of carbon markets, making them more accessible to a wider range of participants.
Climate Change: A global problem that can be solved with collaborative efforts
Climate change is an undeniable reality that poses significant threats to our planet and its inhabitants. The impacts of rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and ecosystem disruptions are felt worldwide.
“Climate change is an existential problem; it is not going away. The sooner we get on the front foot, the sooner we will be able to tackle it”, said Asad.
Recognising the interconnected nature of the climate crisis is essential for fostering international cooperation, sharing responsibilities, and mobilising resources to mitigate and adapt to climate change. In Hirander’s words:
“It is all about bringing the world together into inter-relationships, because climate change is a global problem, and it’s impacting all of us. It needs to transcend those geo-political boundaries for us to really have an impact.”
Through collaborative efforts, we can forge a sustainable path forward, mitigating the impacts of climate change and securing a better future for generations to come.
About citiesabc.com
https://twitter.com/citiesabc_
https://www.instagram.com/citiesabc
About openbusinesscouncil.org
https://www.openbusinesscouncil.org/
https://twitter.com/openbusinesshq
About fashionabc.org
https://www.instagram.com/fashionabcorg/
About Dinis Guarda
https://twitter.com/dinisguarda
https://www.instagram.com/dinisguarda_/
https://openbusinesscouncil.org/wiki/dinis-guarda

Hernaldo Turrillo is a writer and author specialised in innovation, AI, DLT, SMEs, trading, investing and new trends in technology and business. He has been working for ztudium group since 2017. He is the editor of openbusinesscouncil.org, tradersdna.com, hedgethink.com, and writes regularly for intelligenthq.com, socialmediacouncil.eu. Hernaldo was born in Spain and finally settled in London, United Kingdom, after a few years of personal growth. Hernaldo finished his Journalism bachelor degree in the University of Seville, Spain, and began working as reporter in the newspaper, Europa Sur, writing about Politics and Society. He also worked as community manager and marketing advisor in Los Barrios, Spain. Innovation, technology, politics and economy are his main interests, with special focus on new trends and ethical projects. He enjoys finding himself getting lost in words, explaining what he understands from the world and helping others. Besides a journalist, he is also a thinker and proactive in digital transformation strategies. Knowledge and ideas have no limits.