The Metaverse and the new generation of the internet, Web 3.0, are already here. But what exactly is Metaverse? Here’s an infographic that explains all the layered framework of the metaverse: a metaverse that is distinct in architecture and simple in existence.
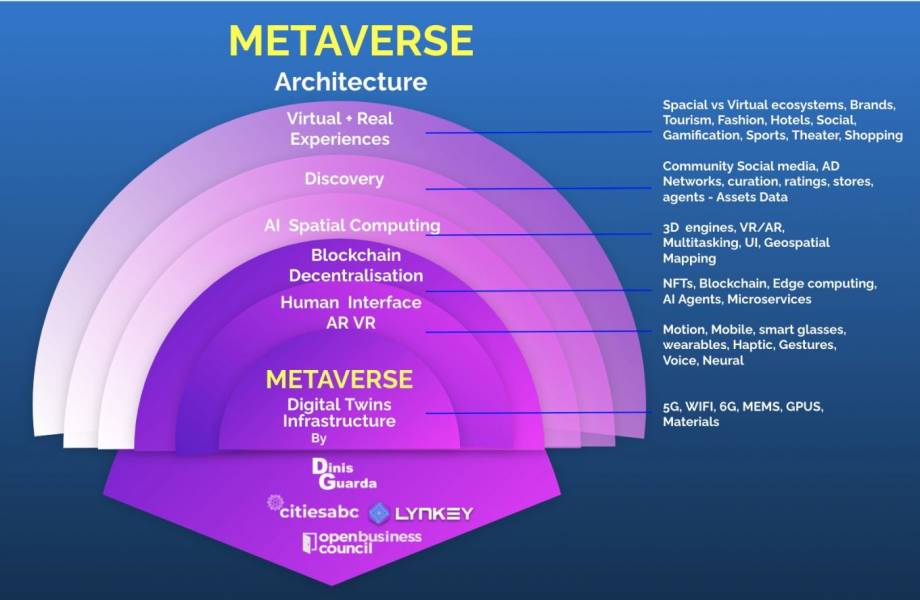
Characterised as a simulated digital environment, Metaverse incorporates technology like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain.
All this, and a realm built on the principles of social media creates a sphere that resembles the real world very closely.
Metaverse is this self-contained virtual economy that is powered by digital currencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
“The metaverse is best understood as the shift of computing and interaction from a device in your pocket into a virtual simulation.” – Matthew Ball, author of “The Metaverse”.
Obviously, there is a need to know this immersive virtual space deep down the intrinsic layers of its architecture, to the very core.
With his expertise in digital and technological advancements and creativity, Dinis Guarda, Founder CEO ztudium, citiesabc explains Metaverse to be layered. Here, he follows a systematic approach to describe the framework of the technology.
Let’s dig through these layers and find out the very essence of the Metaverse.
Experience (Virtual and Real)
Most people, while thinking of the metaverse, focus on this layer- the experiences of interacting while engaging in digitally-driven landscapes, like shopping, games, NFTs, digital media, NFTs, etc.
Perhaps, the popular culture of gaming best describes the features of this evolution- avatar identities, virtual immersion, storytelling, and other social interactions.
Besides this, volumes of data could be generated through everyday experiences too, like office meetings, gym workouts, cooking, tourism, theatre, holiday, or even classroom sessions could be classified under this layer.
Discovery
The information and data are collected either through inbound or outbound sharing or marketing systems.
Inbound discovery includes platforms that are involved in community content. In other words, the places that hold public information of the likes and recommendations by the users are responsible for the inbound discovery, like the social networking sites, app stores, and even search engines.
Outbound discovery, on the other hand, includes notifications and display ads.
In the metaverse, the real-time presence of the users would generate additional data about their physical and social ‘immersiveness’. For instance, during a virtual tour of a property, the systems track a user’s choices, preferences, and dilemmas.
Spatial Computing
It is the technique that blurs the boundaries between the real physical and the virtual world. In other words, constantly blends the two intersecting spheres by manipulating 3D online spaces into uncanny realism, or augmenting the real world with digital experiences.
Advanced technologies like 3D programs and engines, geospatial mapping, AR/VR, and XR have proved useful for spatial computing. Biometric applications, voice recognition, and even gesture recognition are some of the verticals of IoT gaining traction to leverage spatial computing and make the metaverse look more real.
Decentralisation
The key to a successful metaverse lies in its open, decentralised, and distributes nature. With the momentum that blockchain technology has gathered over the past decade, it seems plausible that open-source platforms, smart contracts, a sovereign digital identity, DeFi protocols, and dealing in NFTs are soon to be a consensual choice of the metaverse.
AI agents, Microservices and Edge Computing are going to be the latest trends.
Human Interface
The human-technology interface is getting more illustrious by the day. VR headsets, AR smart devices, neural networks, smart glasses, and other wearables are enhancements to smartphone devices. These merely enhance the human body with digital capabilities.
Digital Twin Infrastructure
It encompasses all the technology that is capable of enabling, connecting, and empowering digital devices. The ultimate goal is to realise the potential earthed within each layer. Data centers, wireless, cloud computing, and related materials and processes make up the infrastructure for digital twin technology.
The Metaverse is already here
With an explosion of technological advancements over the past few years, we are already experiencing the ingression of the metaverse in our lives. Nevertheless, there is still a lot to be learned and evolved. The basic infrastructure already laid down by the wealth of knowledge from thinkers and the pioneers in the metaverse shines brightly to guide humanity towards better frontiers (that are yet to be explored).
How has metaverse transformed different industries? Study suggestion for more information:Top Industries That Will Be Transformed By The Metaverse

Dinis Guarda is an author, academic, influencer, serial entrepreneur, and leader in 4IR, AI, Fintech, digital transformation, and Blockchain. Dinis has created various companies such as Ztudium tech platform; founder of global digital platform directory openbusinesscouncil.org; digital transformation platform to empower, guide and index cities citiesabc.com and fashion technology platform fashionabc.org. He is also the publisher of intelligenthq.com, hedgethink.com and tradersdna.com. He has been working with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, Davos WEF, Philips, Saxo Bank, Mastercard, Barclays, and governments all over the world.
With over two decades of experience in international business, C-level positions, and digital transformation, Dinis has worked with new tech, cryptocurrencies, driven ICOs, regulation, compliance, and legal international processes, and has created a bank, and been involved in the inception of some of the top 100 digital currencies.
He creates and helps build ventures focused on global growth, 360 digital strategies, sustainable innovation, Blockchain, Fintech, AI and new emerging business models such as ICOs / tokenomics.
Dinis is the founder/CEO of ztudium that manages blocksdna / lifesdna. These products and platforms offer multiple AI P2P, fintech, blockchain, search engine and PaaS solutions in consumer wellness healthcare and life style with a global team of experts and universities.
He is the founder of coinsdna a new swiss regulated, Swiss based, institutional grade token and cryptocurrencies blockchain exchange. He is founder of DragonBloc a blockchain, AI, Fintech fund and co-founder of Freedomee project.
Dinis is the author of various books. He has published different books such “4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation”, “How Businesses and Governments can Prosper with Fintech, Blockchain and AI?”, also the bigger case study and book (400 pages) “Blockchain, AI and Crypto Economics – The Next Tsunami?” last the “Tokenomics and ICOs – How to be good at the new digital world of finance / Crypto” was launched in 2018.
Some of the companies Dinis created or has been involved have reached over 1 USD billions in valuation. Dinis has advised and was responsible for some top financial organisations, 100 cryptocurrencies worldwide and Fortune 500 companies.
Dinis is involved as a strategist, board member and advisor with the payments, lifestyle, blockchain reward community app Glance technologies, for whom he built the blockchain messaging / payment / loyalty software Blockimpact, the seminal Hyperloop Transportations project, Kora, and blockchain cybersecurity Privus.
He is listed in various global fintech, blockchain, AI, social media industry top lists as an influencer in position top 10/20 within 100 rankings: such as Top People In Blockchain | Cointelegraph https://top.cointelegraph.com/ and https://cryptoweekly.co/100/ .
Between 2014 and 2015 he was involved in creating a fabbanking.com a digital bank between Asia and Africa as Chief Commercial Officer and Marketing Officer responsible for all legal, tech and business development. Between 2009 and 2010 he was the founder of one of the world first fintech, social trading platforms tradingfloor.com for Saxo Bank.
He is a shareholder of the fintech social money transfer app Moneymailme and math edutech gamification children’s app Gozoa.
He has been a lecturer at Copenhagen Business School, Groupe INSEEC/Monaco University and other leading world universities.




























