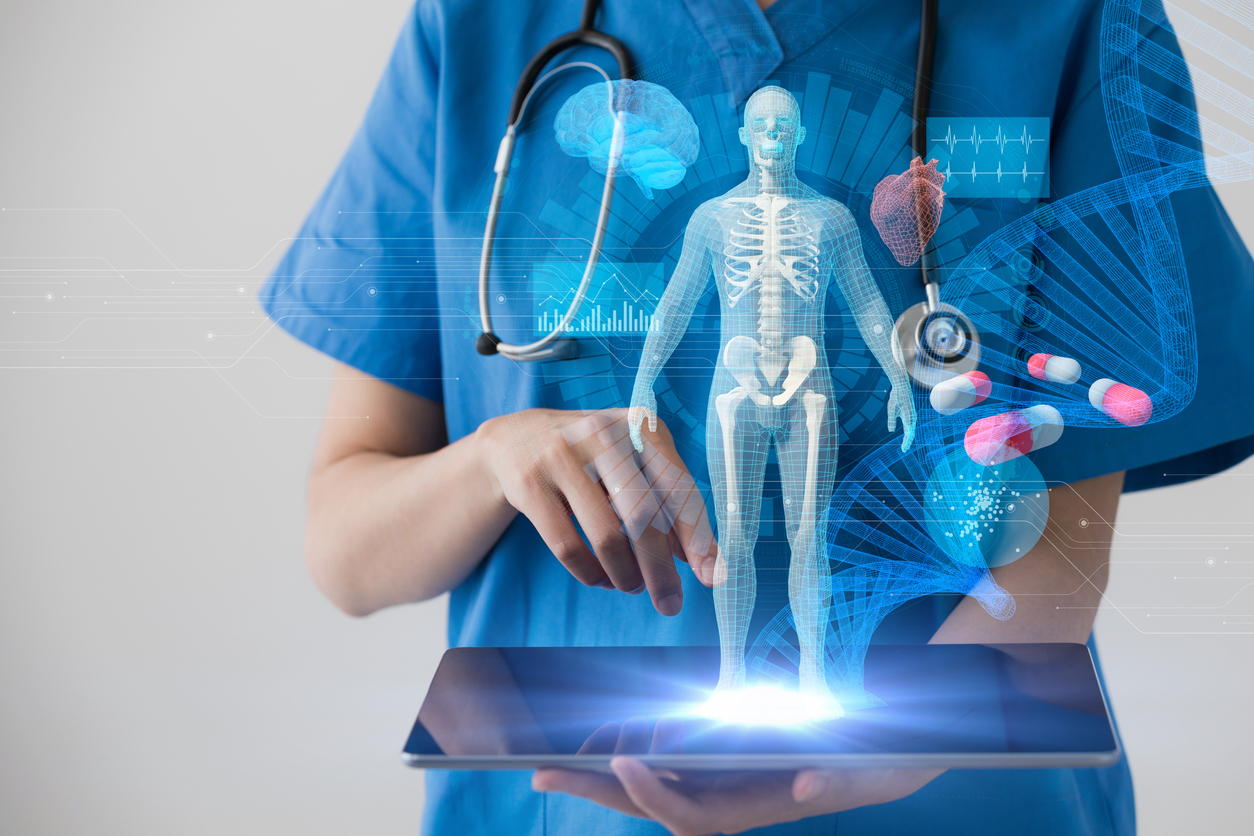
Technology is rapidly changing the world, often in unexpected ways. One such trend is the increasing use of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) in the nursing sector. Together with super computers, machine learning, and smart technology, robots and AI provide invaluable assistance to both nurses and patients in hospitals, care homes, and beyond.
Supply and demand
Nursing in the US and elsewhere is facing an ongoing crisis of supply and demand. The nation is undergoing a combination of factors: the sizeable baby boomer generation is reaching retirement age, and people are living longer due to improved living conditions and medical breakthroughs. These factors have led to an aging population where the number of retirees threatens to outnumber those of working age for the first time. There are more elderly people and more people living with formerly fatal conditions than ever before, and all of these people need either permanent or occasional nursing care.
At the same time, however, there is a shortage of nurses as experienced nursing staff are retiring, and too few young nursing graduates are coming up to replace them. This shortfall means that new nurses are in great demand, and there has never been a better time to consider a career in nursing. Graduates from the Louise Herrington School of Nursing Online at Baylor University are expected to find excellent placements in any one of a large number of nursing positions, both specialist and general.
Technological solutions
In the meantime, various urgent measures are being taken to address the supply crisis, including the use of technological solutions that free existing nurses from arduous, routine, or repetitive tasks, giving them more time to concentrate on taking care of patients. The adoption of robotics and AI in particular has been hastened by the Covid pandemic. Along with telehealth and telemedicine solutions, where AI facilitates remote communication between doctor and patient, robots can be used to administer treatment when it’s unsafe for nurses to be in close contact with a patient due to a high risk of infection.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the leading technological trend of our times. AI-driven health apps are used by nurses, patients, and health-conscious individuals in their own homes to monitor vital signs like pulse, heartbeat, and blood pressure; keep track of diet and exercise; and even detect early warning signs of illness or chronic conditions. Millions of users download and subscribe to the thousands of healthcare apps available online.
AI can also help with analyzing and interpreting the data from scans far faster and with greater accuracy than a human nurse could manage. AI is used to create patient risk profiles and personalized treatment plans as well as to research and create new drugs for rare conditions. AI can reduce the need for unnecessary procedures, saving time and money as well as potential inconvenience and discomfort for the patient.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine, or telehealth, involves conducting consultations, diagnoses, and sometimes treatment remotely. The patients may be in their own homes while a nurse or physician communicates with them from a hospital or office. Sometimes, the procedure may be conducted entirely by AI, with no need for direct involvement from medical professionals at all.
For the patient, this is often more convenient and can be less stressful as they can remain in familiar surroundings. For doctors and nurses, it saves time and money. Increasingly, robots are being incorporated into telemedicine, with telerobotics being considered a field in its own right.
A telepresence robot may be in the same physical space as a patient. Cameras and microphones can function as the eyes, ears, and voice of the doctor or nurse. Using AI, medical personnel may be able to act and communicate independently. AI can also be remote controlled with a nurse speaking through them. Some telepresence robots can detect possible health problems, including depression and anxiety but also some physical ailments, by analyzing the patient’s tone of voice and body movements.
Robot companions
While a robot is no substitute for a living human companion, they can provide solace and comfort to patients who would otherwise be alone for long periods of time. Robots are being used in this way with children, the elderly, and those suffering from conditions like dementia. Sometimes known as socially assistive robots, they can encourage patients to take exercise and remind them to take medication as well as keeping a watchful eye on them.
In pediatrics, nurses sometimes use robot pets to encourage troubled children to overcome hesitation and express their feelings in a positive way. Robotic dogs and cats can interact with children and express a range of emotions, helping them to relearn social skills and creative play. At the same time, robotic pets can monitor their vital signs, make health-related inquiries, and even dispense medication.
Rehabilitation robots
Robotic devices are also used in physical rehabilitation to help nurses to lift and carry patients. These robots usually take the form of AI-empowered exoskeletons that scan the patient’s immediate environment while analyzing and predicting their body movements. Nurses, meanwhile, may use a limited exoskeleton for back support.
In this way, robotics can provide greater patient independence as well as helping to speed up recovery. Physically assistive robots can help disabled individuals to sit, stand, walk, eat, and drink. A modern smart house, full of connected devices equipped with sensors that can help the inhabitant to live independently, could be considered to be a robot as well.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is already a major part of modern nursing, and the medical robotics field is expected to see huge growth over the next twenty years. Existing digital technology like electronic medical records can be integrated with robotics, and robots are already being used for scheduled tasks like the delivery of medicines, supplies, laboratory specimens and patient meals. This frees nurses to spend more time on immediate patient care.
The development of robotics in nursing nevertheless needs to be taken slowly. It’s essential that they are safe and dependable, and that confidential information is kept secure. The perceptions and attitudes of staff, patients, and other stakeholders also need to be considered. Finally, there may be financial, legal, and ethical obstacles to overcome along the way.
Nevertheless, robots and AI remain of great benefit to nurses, taking care of dangerous, repetitive, or physically demanding tasks while also improving patient care and expanding the possibilities of what can be done. In the future, we may see robots and nurses working side by side to provide better care.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems