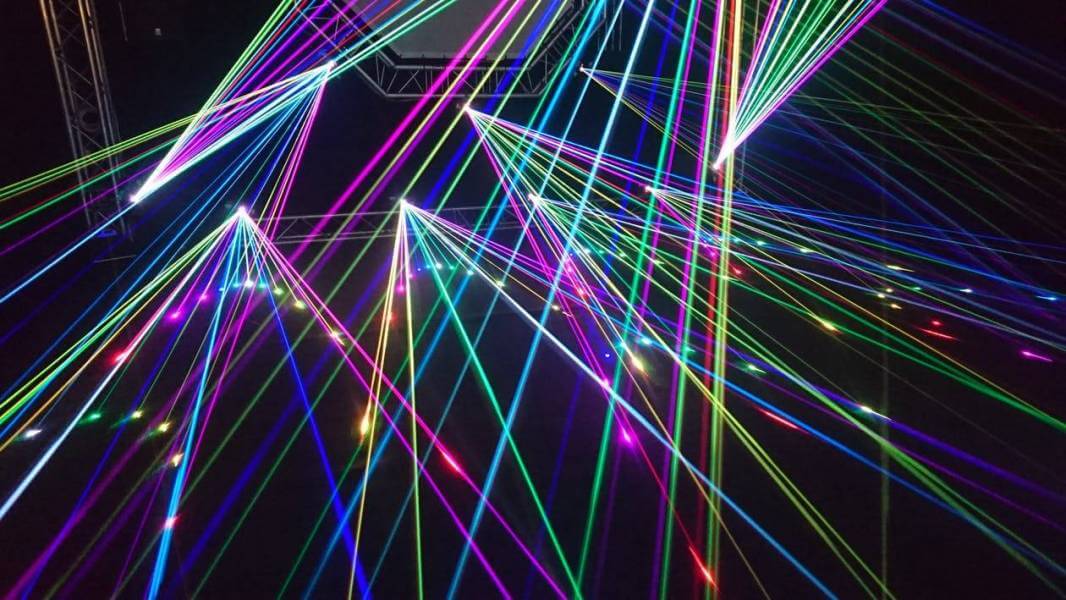
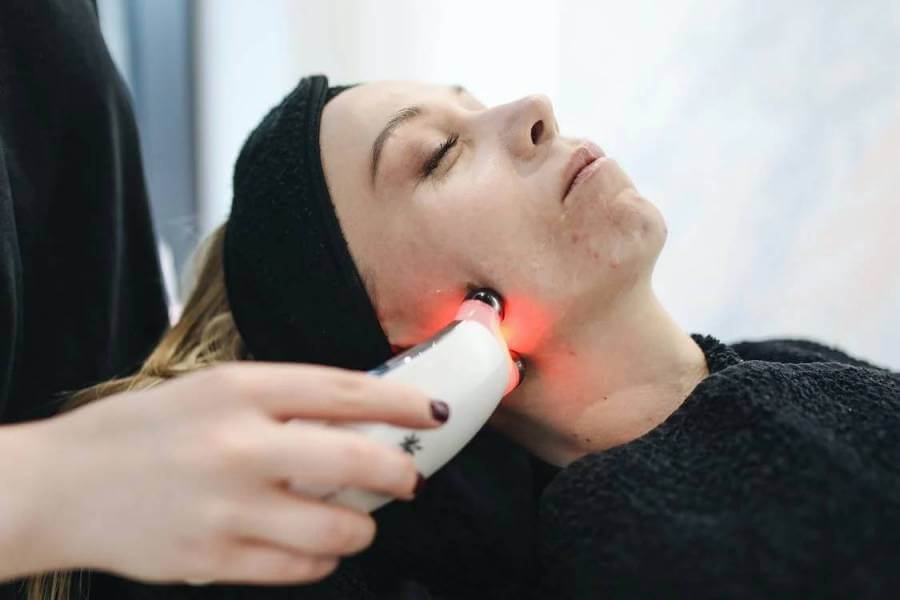
When most people think of lasers, they think of the powerful, destructive beams that can cut through metal. However, lasers come in all shapes and sizes and have a variety of applications. In this blog post, we will be discussing laser diodes – one of the most common types of lasers. We will cover their working principle and characteristics of them, as well as some practical applications.
Everything you should know about laser diodes
It is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. The light is monochromatic, meaning that it has one wavelength. Laser diodes are used in a wide variety of applications, including optical communications, barcode readers, and medical devices. The working principle of a diode is relatively simple. When electric current flows through the device, it causes electrons to flow from the n-type semiconductor to the p-type semiconductor. This creates a diode, which allows the current to flow in one direction only. The electrons that flow into the p-type semiconductor recombine with holes, and this releases energy in the form of photons – which is what we see as light.
How do they work?
Diodes work by using what is known as stimulated emission. This is when electrons in the diode are excited to a higher energy level by an electric current. When these electrons return to their lower energy state, they release photons – which is the light that we see. This stimulated emission or the output of a diode can be controlled by changing the amount of current that is flowing through it. By increasing the current, more electrons are excited and more photons are released, resulting in a brighter beam of light. Conversely, decreasing the current will result in a dimmer beam of light.
What type of diodes can we find?
They are made up of two regions: the P-type region and the N-type region. The P-type region is made up of semiconductor material with a high concentration of holes, while the N-type region is made up of semiconductor material with a high concentration of electrons. When current flows through the diode, it recombines electrons and holes in the junction between the two regions. They also have had a big usage ever since the digital revolution. Anyway, this process emits photons, which are then amplified by mirrors inside the diode to create a beam of light. The wavelength of light emitted by a diode depends on the material used to create it. For example, red diodes typically have wavelengths around 650 nm, while blue diodes have wavelengths around 405 nm.
The classification of diodes
They are classified according to their wavelength. The three main types of diodes are Infrared (IR diodes, visible diodes, and Ultraviolet (UV) diodes.
Infrared diodes have a wavelength of 850-940 nm and are used in fiber optic communications and remote control systems. Visible diodes have a wavelength of 400-700 nm and are used in barcode scanners and optical storage devices. Finally, Ultraviolet diodes have a wavelength of 200-400 nm and are used in medical applications, such as skin treatments.
How do we control the output?
The output can be controlled by changing the current flowing through it. For example, increasing the current will increase the power of the laser beam. However, if the current is too high, it can damage the diode. They also have a threshold current – this is the minimum amount of current required to create lasting action. Once this threshold is reached, increasing the current will not result in any further increase in power.
What are some of the most common characteristics of a laser diode?
They have a number of characteristics that make them well suited for different applications. Each of these characteristics makes them one of the best choices in the matter.
High efficiency
They are more efficient than other types of lasers, making them ideal for use in portable devices.
Low power consumption
They also consume less power than other types of lasers, making them ideal for use in battery-powered devices.
Small size
Small in size, and compact, makes them ideal for use in portable devices.
Fast response time
They also have a fast response time, making them ideal for use in communications applications.
What are some practical applications of laser diodes?
Laser diodes are used in a wide variety of applications, including optical communications, barcode readers, and medical devices. They also have many different applications due to their compact size, efficiency, and low cost. As semiconductor technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more applications for these diodes in the future. As of now, some of the most common places we can find these diodes are:
- Optical communications: Used in fiber-optic communications systems, they are used to transmit information over long distances through optical fibers.
- Barcode readers: As barcode readers, they help scan and decode barcodes. Barcode readers typically use red diodes with wavelengths around 650 nm.
- Medical devices: They are also used in a variety of medical devices, including blood pressure monitors and glucose meters. They are also used in LASIK surgery to correct vision problems.
Are there any limitations to them?
Laser diodes are not perfect and have a few limitations. One limitation is that they can only be used to generate light of a specific wavelength. This means that they can only be used to generate one color of light. Another limitation is that they can be damaged by too much current. If the current flowing through the diode is too high, it can cause the diode to fail. They can be quite expensive, compared to other diodes and they can change their efficiency depending on the temperature.
Despite these limitations, they are still widely used in many different applications due to their high efficiency, low power consumption, and small size. Surely, we can expect to see even more applications for them in the future, as technology expands and finds new ways to do things. For now, these were some of the basic things you should know when it comes to diodes.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems