Smart cities are rapidly becoming the future of urban living. The global market for smart cities is expected to reach $717.5 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 16.5% from 2020 to 2027. With the integration of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics, Smart cities have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 20%, traffic congestion by up to 30%, and crime rates by up to 50%. The World Bank estimates that smart cities can lead to a 10% increase in GDP and a 15% increase in productivity. What could be the possible ways in which we, as stakeholders, could benefit from smart cities?

One of the key features of a smart city is its ability to collect and analyse data from a variety of sources, including sensors, cameras, and other devices. This data is then used to optimize city services and make informed decisions about the allocation of resources. For example, a smart city might use data from traffic sensors to adjust traffic signals in real time, reducing congestion and improving the flow of vehicles.
Smart cities also rely on IoT technologies to connect various systems and devices, allowing for greater efficiency and automation. For example, a smart city might use a network of IoT-connected trash bins to alert sanitation workers when they are full, reducing the need for manual collection while saving time and resources.
In addition to improving the efficiency of city services, smart cities also have the potential to improve the overall quality of life for citizens. For example, a smart city might use data analytics to identify patterns of crime and deploy resources accordingly, reducing the incidence of crime and increasing safety for its citizens. Smart cities might also use data to optimise the distribution of resources such as electricity and water, reducing waste and lowering costs.
An example of the smart city of Singapore
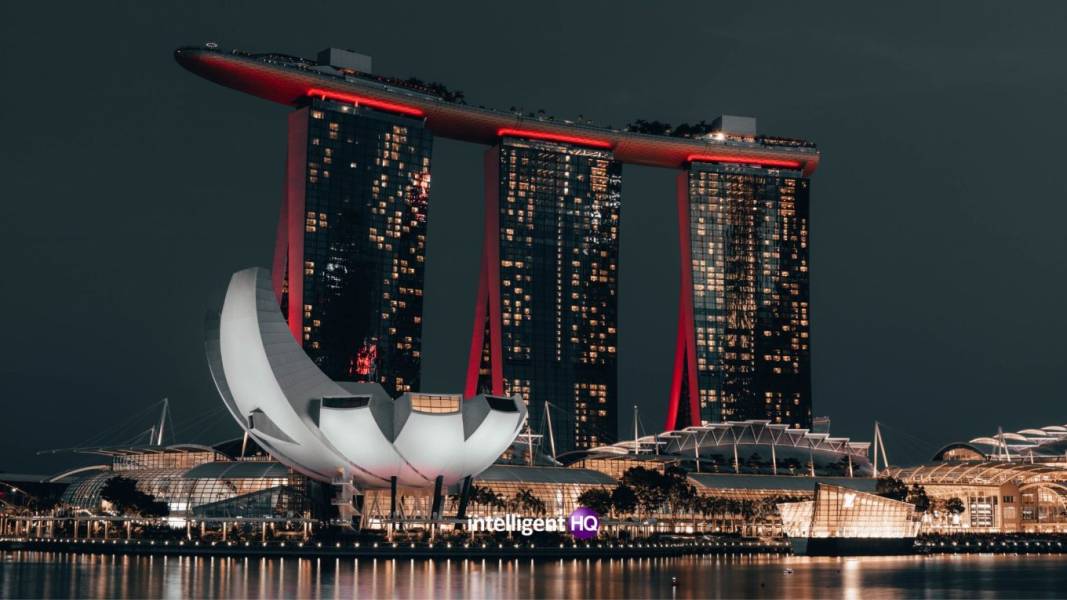

One example of a city that has successfully implemented smart city technologies is Singapore. The city has implemented a range of initiatives, including the use of IoT-connected sensors to regulate traffic flow and manage congestion, as well as the use of data analytics to improve the efficiency of its water distribution system. In addition, Singapore has implemented a comprehensive digital health system, which allows citizens to access medical records and other health information online, improving the efficiency and accessibility of healthcare.
“Singapore is a global leader in the development of smart cities, and our efforts have helped to improve the quality of life for our citizens and make our city more efficient,” says Vivian Balakrishnan, Singapore’s Minister for Foreign Affairs. “By using advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things and data analytics, we are able to optimize city services and make informed decisions about the allocation of resources.”
A sustainable smart city of Amsterdam
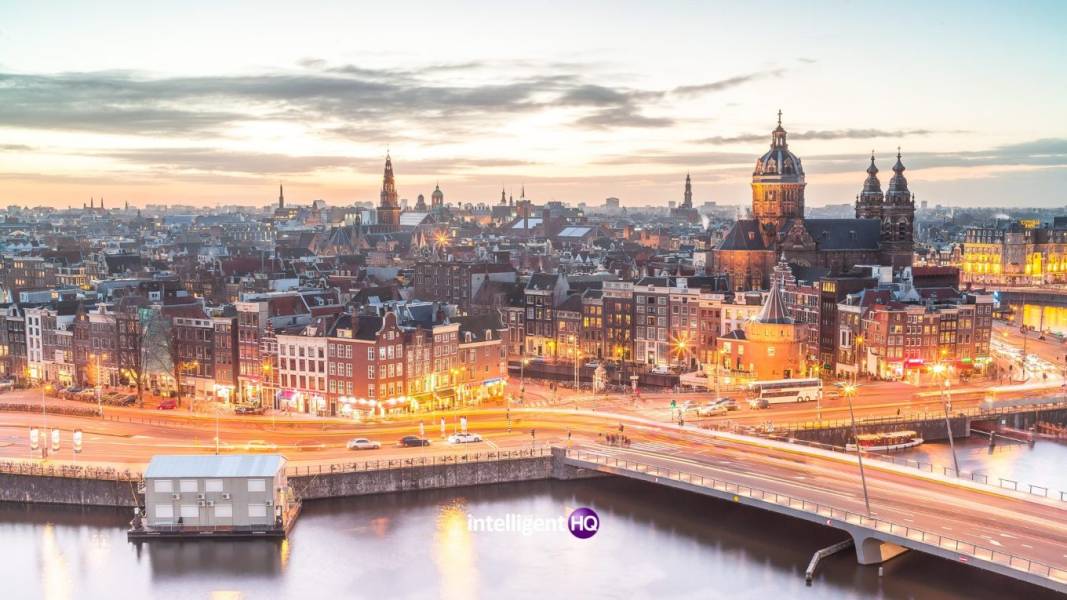

Another example of a smart city is Amsterdam, which has implemented a range of initiatives to improve the sustainability of the city. Amsterdam has installed over 20,000 smart energy meters, which allow residents to track their energy use and make informed decisions about how to reduce their carbon footprint. In addition, the city has implemented a comprehensive smart lighting system, which uses sensors to adjust the intensity of streetlights based on the presence of pedestrians and vehicles.
“Amsterdam is a city that is constantly looking for ways to improve the sustainability of our urban environment,” says Femke Halsema, the Mayor of Amsterdam. “By implementing smart energy meters and a smart lighting system, we are able to reduce our energy consumption and improve the quality of life for our citizens.”
How to invest in smart cities?
There are a few ways to invest in smart cities:
• Platforms like citieasabc provide technology and services for smart cities, like developing IoT sensors, data analytics software, or other technologies that are used to empower smart cities.
• Real estate opportunities in smart cities: As smart cities become more attractive to businesses and residents, investing in real estate properties could benefit the economy of these areas.
• Smart city infrastructure projects: Some governments and companies are looking for private investment to fund smart cities infrastructure projects, such as the development of smart energy grids or smart transportation systems.
• Smart city-focused mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs): These types of investment vehicles allow investors to buy a diverse portfolio of stocks or bonds in companies that are involved in the development of smart cities.
It is important to do thorough research and due diligence before making any investment decisions, as with any other investment. It is also a good idea to seek the advice of a financial advisor or professional investment manager.
Overall, the rise of smart cities represents a significant shift in the way we live and interact with our urban environments. With the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics, cities are able to improve the efficiency of their services and address a range of challenges such as traffic congestion, crime, and environmental sustainability. As more cities adopt smart city technologies, it is likely that we will see a significant impact on the quality of life for citizens around the world.

Peyman Khosravani is a global blockchain and digital transformation expert with a passion for marketing, futuristic ideas, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications. He has extensive experience in blockchain and DeFi projects and is committed to using technology to bring justice and fairness to society and promote freedom. Peyman has worked with international organizations to improve digital transformation strategies and data-gathering strategies that help identify customer touchpoints and sources of data that tell the story of what is happening. With his expertise in blockchain, digital transformation, marketing, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications, Peyman is dedicated to helping businesses succeed in the digital age. He believes that technology can be used as a tool for positive change in the world.