Central Banks’ Blockchain Solutions for Financial Inclusion
All these pilots and early experimentations with blockchain solutions are thought to face the multiple challenges that many times, unfortunately, central banks can’t address. Most notably: Emergent Economies.
The application of DLT and blockchain in emerging economies of developing countries is of great interest to the central banks. In these locations, like in most of Africa, some countries of South America and part of Asia, central banks face greater challenges than their Western counterparts: their populations are mostly unbanked with very limited access to private banking; payments systems work between private financial institutions with little or non-existent communication to Central Banks while most of these payments are done through printed money rather than through electronic solutions. All of these make the role of the Central Banks pretty much inefficient. They can’t control how much money flow is happening between hands, they can’t authorize private banks payments, loans and other services and they can’t effectively control money laundering and other submerged economy that may flourish.
Cambodia is a country that is trying really hard to tackle the unbanked population through blockchain solutions. Most of the people in this country make their payments in cash or mobile-based private applications. They struggle to keep their savings in safe financial banks while they also have difficulties transferring money to those who use a different mobile money application.
“The National Bank of Cambodia will be one of the first countries to use blockchain technology in its national payments systems for use by consumers and commercial banks. It is implementing blockchain technology in the second half of 2019 as an experiment to support both financial inclusion and greater banking system efficiency,” mentioned in the aforementioned WEF report.

Central Banks and Digital Currencies
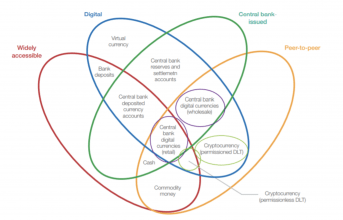
The solutions that central banks are experimenting with vary from one to another. Some focus on developing a national blockchain platform connected to private financial institutions to allow for better communications between them. This would help to authorize and permit legitimate transactions among clients, banks and the central bank. Others try to make their already functioning systems more efficient and fast. And other solutions are a bit more courageous: a blockchain platform thought and deployed to print digital currency that could be equivalent to – and redeemable for – its domestic currency. This method is what is called Central Bank Digital Currency or CBDC.
“Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), a commonly proposed application of blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT), has attracted much interest within the central banking community for its potential to address long-standing challenges such as financial inclusion, payments efficiency, and payment system operational and cyber resilience. Including but not limited to CBDC, central banks are researching and experimenting with at least 10 specific use cases for blockchain and DLT, exploring where they can potentially unlock new possibilities and improve inefficient processes,” said Ashley Lannquist, Project Lead, Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology, World Economic Forum.
Central Banks already issue money electronically, but CBDC, by contrast, is typically issued on distributed ledgers – or blockchain platforms – where it can be transacted in a peer-to-peer manner, facilitating more rapid or cost-efficient transactions in some contexts. CBDC could bring important benefits to a country’s financial system health, including the potential for faster and cheaper domestic and cross-border payments; the improvement of payment system resilience to cyberattacks, operational failures and hardware faults relative to centralized data storage and processing, which has less data redundancy and, therefore, may be less robust or even fostering AML/KYC functionalities and to reduce tax evasion, corruption and illicit activities. A digital currency on a distributed ledger could potentially challenge commercial banks current monopoly, allowing a tighter pressure on commercial banks to increase interest rates to depositors and provide more financial services.
For now, however, these are only experiments and theory but the trend goes towards the adoption of blockchain in central banks. What was seen a few years back as a threat by the IMF and the World Bank, now it has become the latest saviour of a financial system deeply wounded. “Over the next four years, we should expect to see many central banks decide whether they will use blockchain and distributed ledger technologies to improve their processes and economic welfare. Given the systemic importance of central bank processes, and the relative immaturity of blockchain technology, the banks must carefully consider all known and unknown risks to implementation,” concluded the World Economic Forum report.
What is mandatory in the dawn of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is the need of an upgrade – and update – of our current financial services industry. This swift move to the digital must be done in coordination with governments and central banks to keep new and emerging technologies, such blockchain, on the right path. Some Central Banks are speeding up their research, though there is still much left to do. We are still years away to see feasible proposals and, even longer, to deploy them.
Central Banks and Blockchain – Part 1
Resources
Central Banks and Distributed Ledger Technology: How are Central Banks Exploring Blockchain Today?, 2019, WEF.
http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Central_Bank_Activity_in_Blockchain_DLT.pdf/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
Distributed Ledger Technology: beyond blockchain, 2016, UK Government Chief Scientific Adviser.
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/492972/gs-16-1-distributed-ledger-technology.pdf/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
BOJ/ECB joint research project on distributed ledger technology, 2018, European Central Bank.
https://www.ecb.europa.eu/pub/pdf/other/stella_project_leaflet_march_2018.pdf/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
istributed ledger technical research in Central Bank of Brazil, 2017, Banco Central do Brazil. /. Accessed 30th April 2019.
A Statement on Launching “Aber” Project, the Common Digital Currency between Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) and United Arab Emirates Central Bank (UAECB) 2019, sama.gov.sa.
http://www.sama.gov.sa/en-US/News/Pages/news29012019.aspx/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
Survey on the digital revolution in the French banking sector, 2018, Banque de France. https://acpr.banque-france.fr/sites/default/files/medias/documents/194ta18_as_88_etude_revolution_numerique_secteur_bancaire_francaisv2_so.pdf/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
Lannquist,Ashley. Central Banks and Distributed Ledger Technology: How are Central Banks Exploring Blockchain Today, 2019, WEF.
http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Central_Bank_Activity_in_Blockchain_DLT.pdf/. Accessed 30th April 2019.
What is a Central Bank Definition and Role, 2019, thebalance.com.
https://www.thebalance.com/what-is-a-central-bank-definition-function-and-role-3305827/. Accessed 10th June 2019.
IMF launches Private Blockchain Based Crypto After Bashing Bitcoin, 2019, newsbtc.com.
https://www.newsbtc.com/2019/04/13/imf-launches-private-blockchain-based-crypto-after-bashing-bitcoin/. Accessed 10th June 2019.
Over Central Banks are Considering Blockchain Currencies Davos Report, 2019, coindesk.com.
https://www.coindesk.com/over-40-central-banks-are-considering-blockchain-currencies-davos-report?es_p=8998601/, Accessed 10th June 2019.

Dinis Guarda is an author, academic, influencer, serial entrepreneur, and leader in 4IR, AI, Fintech, digital transformation, and Blockchain. Dinis has created various companies such as Ztudium tech platform; founder of global digital platform directory openbusinesscouncil.org; digital transformation platform to empower, guide and index cities citiesabc.com and fashion technology platform fashionabc.org. He is also the publisher of intelligenthq.com, hedgethink.com and tradersdna.com. He has been working with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, Davos WEF, Philips, Saxo Bank, Mastercard, Barclays, and governments all over the world.
With over two decades of experience in international business, C-level positions, and digital transformation, Dinis has worked with new tech, cryptocurrencies, driven ICOs, regulation, compliance, and legal international processes, and has created a bank, and been involved in the inception of some of the top 100 digital currencies.
He creates and helps build ventures focused on global growth, 360 digital strategies, sustainable innovation, Blockchain, Fintech, AI and new emerging business models such as ICOs / tokenomics.
Dinis is the founder/CEO of ztudium that manages blocksdna / lifesdna. These products and platforms offer multiple AI P2P, fintech, blockchain, search engine and PaaS solutions in consumer wellness healthcare and life style with a global team of experts and universities.
He is the founder of coinsdna a new swiss regulated, Swiss based, institutional grade token and cryptocurrencies blockchain exchange. He is founder of DragonBloc a blockchain, AI, Fintech fund and co-founder of Freedomee project.
Dinis is the author of various books. He has published different books such “4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation”, “How Businesses and Governments can Prosper with Fintech, Blockchain and AI?”, also the bigger case study and book (400 pages) “Blockchain, AI and Crypto Economics – The Next Tsunami?” last the “Tokenomics and ICOs – How to be good at the new digital world of finance / Crypto” was launched in 2018.
Some of the companies Dinis created or has been involved have reached over 1 USD billions in valuation. Dinis has advised and was responsible for some top financial organisations, 100 cryptocurrencies worldwide and Fortune 500 companies.
Dinis is involved as a strategist, board member and advisor with the payments, lifestyle, blockchain reward community app Glance technologies, for whom he built the blockchain messaging / payment / loyalty software Blockimpact, the seminal Hyperloop Transportations project, Kora, and blockchain cybersecurity Privus.
He is listed in various global fintech, blockchain, AI, social media industry top lists as an influencer in position top 10/20 within 100 rankings: such as Top People In Blockchain | Cointelegraph https://top.cointelegraph.com/ and https://cryptoweekly.co/100/ .
Between 2014 and 2015 he was involved in creating a fabbanking.com a digital bank between Asia and Africa as Chief Commercial Officer and Marketing Officer responsible for all legal, tech and business development. Between 2009 and 2010 he was the founder of one of the world first fintech, social trading platforms tradingfloor.com for Saxo Bank.
He is a shareholder of the fintech social money transfer app Moneymailme and math edutech gamification children’s app Gozoa.
He has been a lecturer at Copenhagen Business School, Groupe INSEEC/Monaco University and other leading world universities.










