Throughout the centuries, humans have made tremendous leaps forward in the way we build, interact, and communicate with each other and the world. More recently we have shifted from an age of industrialisation into the age of information, where we now have an unlimited amount of knowledge available at our fingertips. The advancements we are making in technology are now developing at a rate faster than ever before, blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological realms. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect it to impact all aspects of our lives and society as a whole. It then begs us to ask the question “what does our future look like?”
Below we take a look at 5 technologies that exist today which are paving the way for tomorrow’s future
1. Artificial Intelligence
We’ve all seen sci-fi movies about an AI that threatens to overturn the human race and take over after developing a mind of its own….but that’s not quite the reality of it. AI has been around for decades, albeit on a simpler scale, being used in applications such as video games, fraud protection, and spam detection in your emails. There is a very real and practical use for AI and it is now evolving faster than ever, being applied in numerous ways to improve the lives of individuals and business operations. From your virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri or Google’s Home, to Netflix suggesting movies for you, web support chat bots, or the estimated delivery time of your Uber Eats, these systems help to answer your questions, take your requests and make your life easier. Designed to learn more about you in order to make better and more accurate suggestions for you, these AI need to collect data from search histories, products purchased, or even overheard conversations, to discover your preferences. We won’t touch on the privacy issues here…
Considering bigger developments, autonomous vehicles have been in development for a while, and it’s not as far away as you might think. Many companies are working on this and Google is already working on an algorithm that allows an AI to learn to drive through experience, just as humans do. There could be many benefits to autonomous vehicles including fewer road accidents, more efficient fuel consumption and reduced traffic congestion to name a few. Within healthcare, professionals are working to try connect AI with the neural network of an amputees brain, so they are better able to communicate with the attached prosthesis, giving the user better control.
While the future applications of AI are anticipated to help make our lives easier and more efficient, there is caution among some of not only the reliance on this technology, but the number of jobs that will replace humans. Some of these are already integrated into everyday life, including self-serve checkouts, online support, and other roles that can adequately be handled at a much smaller cost using AI. However, not all see the growth of this industry as ‘humans vs. AI’, instead they see the integration of both to create a better us and a better world.

2. Distributed Ledger Technology
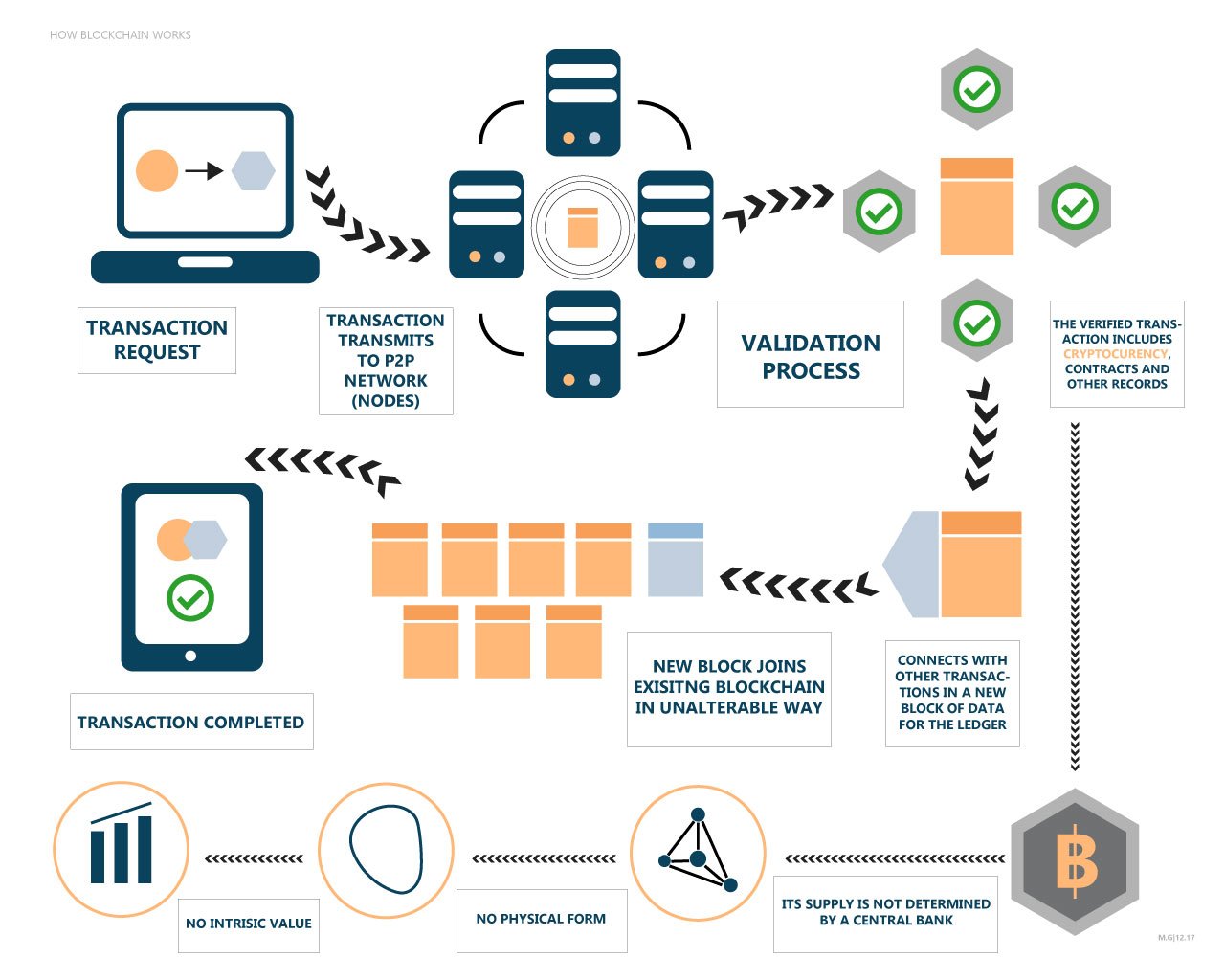
Distributed Ledger Technology, more commonly referred to as Blockchain, is another more recent technology set to disrupt most industries worldwide. Blockchain was developed, along with its first application, Bitcoin, to disrupt the financial industry. It served the purpose of establishing a trustless economy through its cryptography and decentralised components, rendering the need for third parties of traditional financial transactions useless. Blockchain’s 3 main features: decentralisation, transparency, and security, aimed to make the financial industry more secure while reducing fees, allowing for faster transactions, and free from control by a single point of authority.
However, Blockchain technology has become much more than just a solution for financial services. The same features that are improving the deficits of the financial services industry have the ability to resolve the inefficiencies of almost every other industry. Not only has it allowed us to digitise money, which is not a new concept, but we can now place both physical and intangible assets such as copyrights, commodities, or land ownership rights on to the blockchain for secure proof of ownership and easier transferability.
We are also seeing supply chain management of food, retail, logistics, and construction industries being redesigned through transparent and immutable record keeping, allowing a purchaser to know the quality and origin of the product they are buying.
The implications for the healthcare industry are immense, and can help create a universal information system with easier and more secure access to records, research, available therapies along with patients’ data, while minimising administration time. Smart contracts are able to self execute functions when certain conditions are met that remove the need for a lawyer or other intermediary which in turn is also driving down costs.
Additionally, Blockchain is also enabling us to move from an ownership economy to a shared economy where we no longer need to own our own items but are able to share resources including cars, data storage, internet, solar and more.
Although Blockchain is still in its infancy, and requires further regulation, there is no doubt that this technology will continue evolving to play a significant role in transforming inefficient and outdated business practices and redistributing wealth and rights back to the people.
3. 3D Printing
From printing novelty objects, to hearing aids, to prosthetic limbs and all the way to spacecraft engines, the area of 3D printing technology is quickly securing its place in the future of manufacturing. 3D printing has been around since the 1980’s but in recent years has become more readily accessible and is changing the way we manufacture on a large scale. The many benefits of this technology see faster builds that are cheaper and less wasteful of resources, while being customisable and complex in nature. What’s more, it enables conceptual designs to be printed to give an architect, client, or shareholder a complete picture of the end product, which minimises miscommunication or risk of a finished product not matching the design.
One of the ways in which we have already seen a practical and effective application is in prosthetics. The ability to print prosthetics using 3D printing technology not only substantially reduces the cost by thousands, thereby making it more affordable, but its customizability allows it to be a more precise fit for the individual user. Elon Musks’ space company Space X used 3D printing to create the engine chambers of one of their engines for their spacecraft Dragon. By using 3D printing it took only 3 months from concept to completion to design this, drastically reducing lead-time. The airline industry is also looking into the future benefits of manufacturing using 3D printers, most notably Singapore Airlines Engineering Company, who have partnered with Stratasys and are considering opening a facility to look into the benefits of manufacturing aircraft parts.
3D printing is now starting to turn heads within the construction industry as basic housing and buildings are being built on budgets as low as $2000 USD for a basic house. The construction industry is realising the benefits of more efficient use of resources, less wastage, less pollution on the environment, as well as better health and safety. While it is not yet practical for detailed and complex building projects, we are seeing the benefits of 3D printing houses in areas of relief aid, where communities are left homeless after areas have been destroyed.

4. Virtual Reality/Augmented Reality
These technologies are becoming increasingly popular within the entertainment industry as they help blur the lines of the physical and digital worlds. More interactive gameplay is now possible, and the success of Pokemon Go where augmented reality allowed you to catch Pokemon on your mobile while walking through the streets, showed that everyday people are willing and ready to use it. Now, gaming companies are renting warehouses for interactive gaming, allowing players to fight against a Zombie apocalypse and all encapsulated within a VR headset.
Tech giants are also developing VR/AR technologies to integrate into their own product offerings including Apple’s ARKit, Google’s ARCore or VR Project Cardboard, Oculus’ Rift, and PlayStationVR to name a few. While VR and AR are most notably thought of for its ability to transform the entertainment industry to new levels, there are a number of cases for its application in other industries including healthcare, travel, education, architectural design, sports, and more. A shift in the construction industry is also expected with the development of VR, AR, and MR (mixed reality), combining with existing software to help architects and 3D designers better understand and design their projects, showcasing them to their clients and shareholders in real time.
Combining VR with software like BIM and technologies like Big Data will also enable the the onsite construction to become more efficient through more accurate evaluations of the build and modeling behaviours. Worth a combined 6.1 billion US dollars in 2016, the combined VR/AR market is expected to grow to 215 billion by 2021.

5. Internet of Things
The internet of things (IoT) is an expansive network of “things”, or devices which are connected to the internet and therefore able to connect and communicate with each other. It is another technology that will help to bridge the gap between the physical and digital spheres. There were 17 billion connected devices in 2016 and the projection for 2020 spans anywhere from 28 to 100+ billion. The ability to have devices connect to the internet is nothing new, but we are now connecting more “things” to the internet than ever before, from your toaster to you front door, and what’s more we’re connecting those devices to each other.
Imagine your alarm going off in the morning and prompting your coffee maker to start brewing your morning cup. The IoT will see new relationships develop between things-things, things-people, and people-people, all to make our lives easier. We already see this now, for example we can control our smart heating on from our phones so it’s at the ideal temperature when you walk through your front door. Future developments could see our cars connect with our calendars to auto navigate us to our destination in the most time efficient route, or our fridge ordering your groceries when running low.
On a more global scale, the IoT will eventually transform our cities into “smart cities”. With the help of sensors, the IoT will make our cities a more efficient, cost effective, and safer place to live. Smart buildings will turn facilities off when closed, and turn everything back on when it opens. Smart street lights will turn off when no one is passing through. Smart infrastructure will allow us to detect faults or deterioration in city infrastructure or contamination in water supplies, and smart grids can use and distribute energy more efficiently throughout the city. Driverless cars will be able to connect to smart traffic sensors to determine the most efficient route possible, they may also be able to connect with sensors built into sidewalks to determine where there are spare parks.
Of course this is a long way off happening, and requires much of our existing infrastructure to be replaced, but it is an anticipated idea of how the IoT can be used to improve our cities. With a projected global worth of 6.2 trillion USD by 2025, we can expect most industries to be impacted by the IoT, most notably the healthcare sector, which will see improvements in diagnoses and treatments, and monitoring of our own health.

While we can only predict what our future will look like, we can start to see that the possibilities are endless, and that we are only beginning to see a small fraction of what may be to come. One thing that we can be sure of, however, is that it’s going to change society as we know it today. However, with so much of our lives expected to be reliant on technology, we must be aware of the possible vulnerabilities with so much of our data being stored.
Additionally, a digital society poses a greater risk for a single hack to have drastic implications. There are many differing opinions on the future of technology and how it will impact our lives, some saying it will help drive us into the future, driving productivity, helping us live longer, and increasing efficiencies, while others see it as a destructive catalyst that will break down society and humanity as we know it. The more likely reality is that we will experience both positive and negative implications from the advancement in technology, just as both exist in any other setting.
Passionate speaker, digital technology blogger, and founder of the community Tech Talk Berlin. Coffee lover and sucker for cat videos on YouTube. Lauren has been working in business development for a number of Blockchain companies, most notably Kora where she works as Chief Administrative Officer. She creates, edits, and advises on white paper content and business strategy across a number of startups, and writes about technologies leading innovation and their applications in our future.