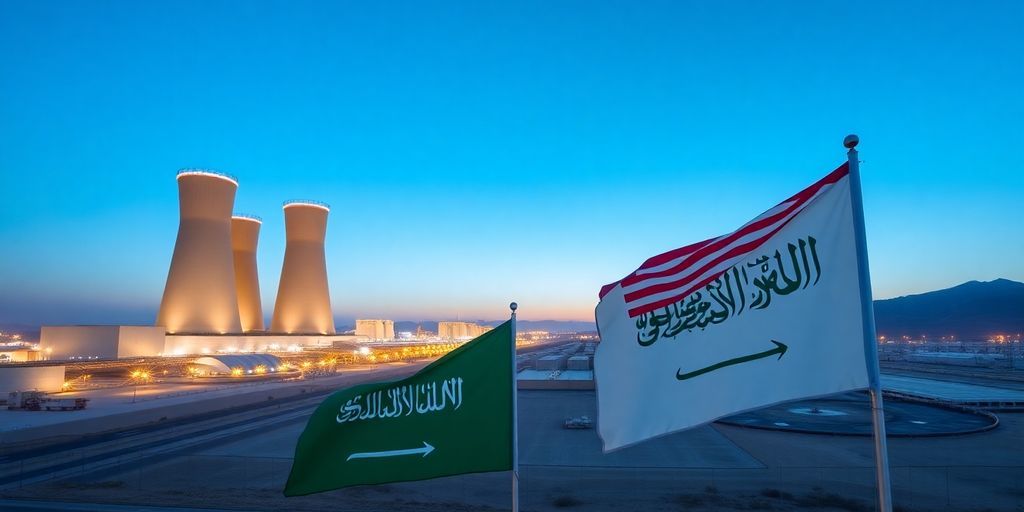
The United States and Saudi Arabia have reignited discussions regarding the transfer of nuclear technology, aiming to establish a commercial nuclear power industry in the kingdom. Energy Secretary Chris Wright announced a potential pathway for an agreement that could allow Saudi Arabia to enrich uranium, a move that has significant geopolitical implications.
Key Takeaways
- U.S. and Saudi Arabia are in talks to develop a civil nuclear program.
- The agreement could allow Saudi Arabia to enrich uranium domestically.
- Previous negotiations stalled due to concerns over nuclear weapons proliferation.
- The deal is seen as part of broader U.S.-Saudi relations, including potential normalization with Israel.
Background of the Talks
For years, Saudi Arabia has sought U.S. assistance in developing its nuclear energy capabilities as part of its strategy to diversify its economy beyond oil. The discussions had previously stalled due to Saudi Arabia’s reluctance to accept stringent nonproliferation conditions, particularly regarding uranium enrichment.
Energy Secretary Chris Wright emphasized the importance of U.S. involvement, stating, "It’s critical that it becomes the United States as the partner." He noted that the U.S. aims to ensure that any nuclear program in Saudi Arabia adheres to high nonproliferation standards.
Current Developments
During his recent visit to Riyadh, Wright indicated that both nations are on a "pathway" to an agreement that would facilitate cooperation in developing Saudi Arabia’s nuclear capabilities. He mentioned that further details regarding a memorandum of understanding would be forthcoming later this year.
The proposed agreement would likely involve a 123 agreement under the U.S. Atomic Energy Act, which governs nuclear cooperation between the U.S. and other countries. This agreement is crucial for allowing U.S. companies to engage in nuclear projects in Saudi Arabia.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the optimism surrounding the talks, several challenges remain:
- Nonproliferation Concerns: The U.S. requires strict adherence to nonproliferation standards, which may limit Saudi Arabia’s ability to enrich uranium.
- Congressional Approval: Any agreement will need to be reviewed and approved by Congress, where there is bipartisan skepticism regarding the potential risks of nuclear proliferation in the region.
- Regional Tensions: Saudi Arabia’s nuclear ambitions are closely tied to its rivalry with Iran, which complicates the negotiations. Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman has previously stated that Saudi Arabia would pursue nuclear weapons if Iran does.
Broader Implications
The revival of these talks comes at a time when the geopolitical landscape in the Middle East is shifting. The Biden administration had previously linked nuclear cooperation with Saudi Arabia to the kingdom’s willingness to normalize relations with Israel. However, recent conflicts, including the Israel-Hamas war, have complicated these dynamics.
Wright’s visit also included discussions on energy cooperation beyond nuclear technology, focusing on critical minerals and climate change initiatives. The U.S. aims to strengthen its partnership with Saudi Arabia, which is vital for both energy security and economic stability in the region.
Conclusion
As the U.S. and Saudi Arabia move forward with nuclear technology discussions, the outcome will have significant implications for regional security and energy policy. The potential for a nuclear partnership reflects a broader strategy to enhance cooperation between the two nations while navigating the complexities of Middle Eastern geopolitics.
Sources
- U.S. Revives Talks With Saudi Arabia on Transfer of Nuclear Technology, The New York Times.
- Saudi Arabia, US in talks to sign deal on nuclear technology, Mehr News Agency.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems