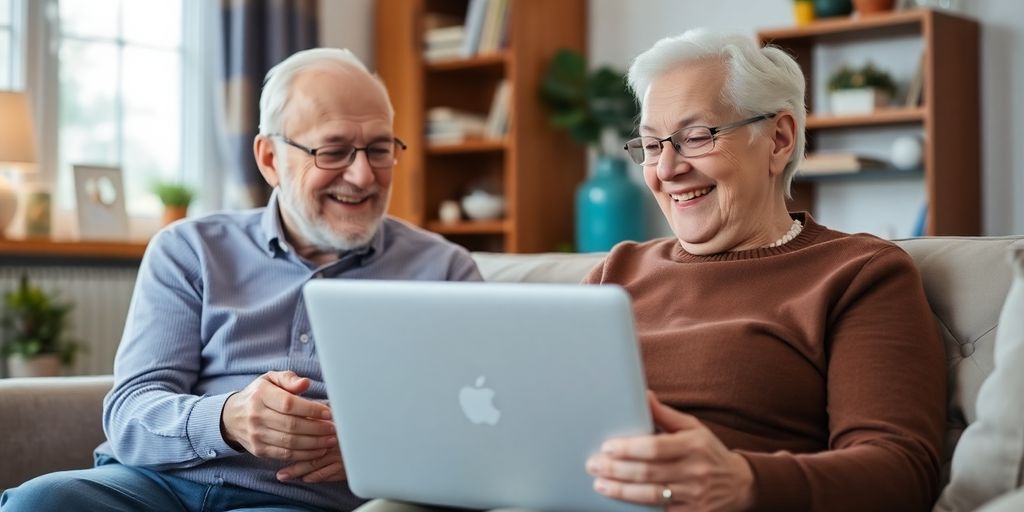
Recent studies have revealed a surprising connection between technology use and cognitive health in older adults. Contrary to fears of "digital dementia," research indicates that engaging with digital technology may actually reduce the risk of cognitive decline among seniors. This finding is particularly significant as the first generation raised with technology enters their golden years.
Key Takeaways
- Increased technology use is associated with a 58% lower risk of cognitive decline.
- The study analyzed data from over 411,000 adults aged 50 and older.
- Engaging with technology may enhance cognitive resilience and social connectivity.
The Digital Dementia Hypothesis
The term "digital dementia" was coined to describe concerns that reliance on technology could weaken cognitive abilities. Critics argue that increased screen time and reliance on devices for memory tasks could lead to cognitive decline. However, recent research challenges this notion, suggesting that technology may instead foster cognitive engagement.
Study Overview
A comprehensive meta-analysis conducted by researchers from Baylor University and the University of Texas at Austin examined 57 studies involving more than 411,000 participants. The analysis focused on the relationship between technology use and cognitive decline, measuring outcomes such as performance on cognitive tests and diagnoses of dementia.
- Findings: The study found that higher technology use correlated with a 58% reduction in the risk of cognitive impairment.
- Control Factors: The results remained significant even after accounting for variables like socioeconomic status, education, and overall health.
Cognitive Benefits of Technology Use
The researchers propose that using technology may provide cognitive benefits similar to those gained from physical activity. Engaging with digital devices requires problem-solving skills and adaptability, which can stimulate cognitive function. For many older adults, learning to navigate new software or troubleshoot issues can be a mentally challenging task that promotes brain health.
Social Connectivity and Independence
In addition to cognitive benefits, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing social connections among older adults. Video calls, social media, and messaging apps allow seniors to maintain relationships with family and friends, reducing feelings of isolation. This social engagement is linked to better cognitive health and may help mitigate the risks associated with loneliness.
The Role of Digital Scaffolding
Digital tools can also serve as a form of "digital scaffolding," helping older adults maintain independence despite cognitive challenges. Features like reminders, GPS navigation, and online banking can support daily living activities, allowing seniors to manage their lives more effectively even as cognitive abilities decline.
Conclusion: Embracing Technology for Better Brain Health
The findings from this study suggest that technology use, when approached mindfully, can be beneficial for cognitive health in older adults. While it is essential to avoid mindless scrolling and excessive screen time, engaging with technology in meaningful ways can enhance cognitive resilience and social connectivity. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, fostering a healthy relationship with technology may be key to supporting the cognitive health of future generations of seniors.
Sources
- A meta-analysis of technology use and cognitive aging, Nature.
- New study finds no evidence technology causes ‘digital dementia’ in older people, The Conversation.
- Digital technology use linked to lower risk of cognitive decline, News-Medical.
- Technology use may lower risk for dementia, study finds, CNN.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems