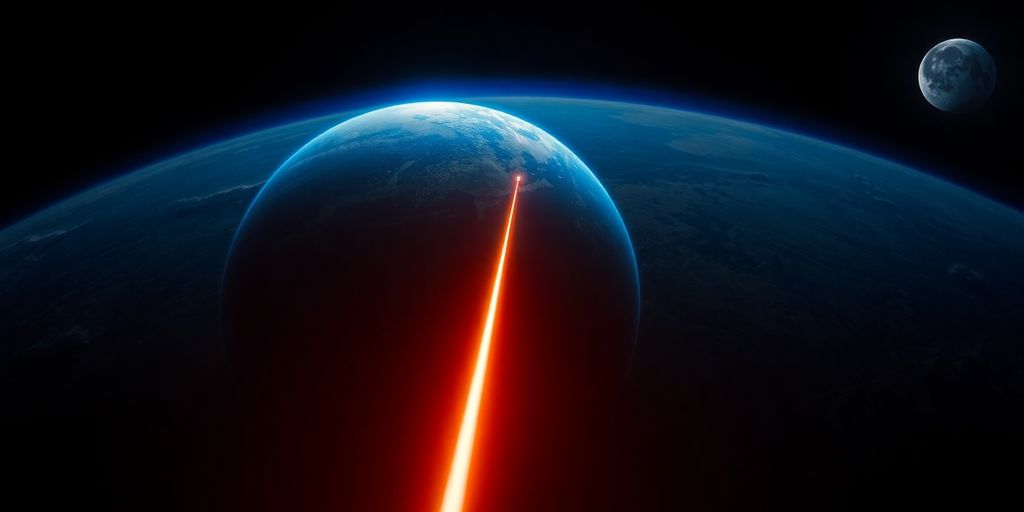
In a groundbreaking achievement, China has successfully measured the distance between the Earth and the Moon using its own laser technology for the first time. This significant milestone showcases China’s advancing capabilities in space science and marks a new era in lunar exploration.
Key Takeaways
- China independently measures Earth-Moon distance using laser technology.
- The measurement was conducted during daylight, overcoming previous limitations.
- This technology enhances navigational precision for future lunar missions.
- It signifies China’s growing independence in space measurement capabilities.
The Breakthrough: Daytime Lunar Laser Ranging
Chinese scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have achieved what was once deemed impractical: conducting lunar laser ranging during daylight hours. This unprecedented capability allows for continuous lunar navigation, which is crucial for upcoming missions.
Dr. Li Wei, the lead scientist at the Chinese lunar research division, stated, "This achievement represents a quantum leap in our space measurement capabilities. By successfully ranging the Moon during daylight, we’ve effectively created the possibility for 24/7 lunar navigation."
How the Technology Works
The process involves sending high-powered laser pulses toward reflectors left on the lunar surface by previous missions. The pulses bounce back to Earth, and by precisely calculating the round-trip time, scientists can determine the exact distance between our planet and its satellite with millimeter-level accuracy.
Key features of this technology include:
- Advanced Infrared Laser Technology: This allows for precise measurements even in bright daylight.
- Ultra-Sensitive Detectors: Capable of isolating weak returning signals from overwhelming solar background noise.
Strategic Importance for China’s Space Ambitions
This technological achievement has profound implications for China’s position in the global space race, particularly as it plans for summer exploration missions. The benefits include:
- Enhanced navigational precision for the Chang’e lunar missions.
- Critical support for the planned China-Russia Moon base.
- Improved satellite positioning systems.
- Independence from foreign space measurement data.
Scientific Applications Beyond Lunar Exploration
The laser ranging technology not only aids lunar exploration but also has broader scientific applications. Professor Zhang Mei from the Beijing Space Institute noted, "Much like how medical researchers are using nanotechnology to make breakthroughs, our laser ranging technology provides unprecedented precision."
This technology allows for detailed studies of:
- Earth’s rotation
- Tectonic movements
Global Implications and Technological Sovereignty
China’s achievement reflects a broader trend towards technological self-reliance, similar to its advancements in AI and healthcare. The new laser ranging capability reduces dependency on NASA and ESA measurements, strengthens China’s position in space collaboration negotiations, and demonstrates technological parity with established space powers.
Future Prospects: Beyond the Moon
As China’s space program continues to evolve, the same laser ranging technology could potentially be adapted for Mars and other deep space destinations. This achievement comes at a time when global space exploration is intensifying, with AI technologies increasingly supporting missions and navigation.
As summer missions prepare for launch, China’s new capability ensures it remains at the forefront of this new era of space exploration. This breakthrough serves as a reminder that humanity’s expansion into space is accelerating, with new players bringing innovative solutions to the challenges of cosmic measurement and exploration.
Sources
- China measures Earth-Moon distance independently with laser technology for the first time, Journée Mondiale.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems