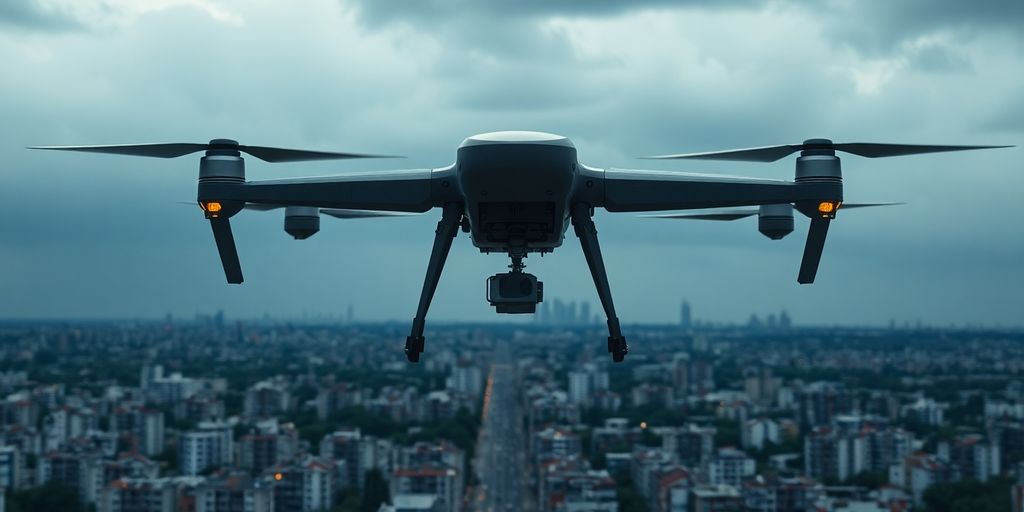
The United Nations has recently emphasized the urgent need for regulations governing military technologies that utilize artificial intelligence (AI). As discussions unfold at the UN General Assembly, experts warn that the rapid advancement of autonomous military systems poses significant risks to global security and humanitarian principles.
Key Takeaways
- The UN is advocating for global regulations on AI-powered military technologies.
- Experts highlight the potential dangers of unregulated autonomous weapons, often referred to as "killer robots."
- Secretary-General António Guterres calls for clear rules to prevent geopolitical divides and ensure ethical use of AI in warfare.
The Growing Concern Over Autonomous Weapons
The integration of AI into military operations has accelerated, leading to concerns about the implications of autonomous weapons systems. These technologies, capable of making decisions without human intervention, could fundamentally alter the nature of warfare.
- Potential Risks:
- Increased likelihood of unintended engagements.
- Difficulty in assigning accountability for actions taken by autonomous systems.
- The potential for escalation in conflicts due to rapid decision-making capabilities.
Experts like Robert Bishop, vice chancellor at Texas A&M University, have voiced their concerns at the UN, stating that the pace of technological advancement has outstripped existing policies and regulations. He emphasized the need for a framework that ensures these technologies are used ethically and responsibly.
The Call for Global Regulations
During the recent UN summit, Secretary-General Guterres highlighted the necessity of establishing global guardrails for AI technologies in military applications. He warned that without regulation, the proliferation of these systems could exacerbate existing geopolitical tensions.
- Key Points from Guterres:
- The need for a legally binding agreement on AI weapons by 2026.
- The importance of addressing human rights and ethical considerations in the development of military AI.
- The goal of preventing a divide between nations that possess advanced AI capabilities and those that do not.
Ethical Approaches to AI in Warfare
Bishop proposed that AI could be harnessed to reduce conflict through non-lethal means. He suggested that AI technologies could assist policymakers in making informed decisions that prioritize peace over aggression.
- Examples of Ethical AI Use:
- Analyzing data to identify non-violent solutions to potential conflicts.
- Enhancing cybersecurity measures to protect against malicious actors.
The Future of Military AI Regulation
As discussions continue, the UN aims to bring together various stakeholders, including governments, civil society, and industry leaders, to address the challenges posed by autonomous weapons. The first international meeting focused on these issues has already taken place, marking a significant step towards establishing a comprehensive regulatory framework.
- Next Steps:
- Continued dialogue among 96 participating countries.
- Development of ethical guidelines for AI use in military contexts.
- Emphasis on collaboration to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
In conclusion, the UN’s call for urgent regulation of military AI technologies reflects a growing recognition of the complexities and risks associated with autonomous weapons. As the landscape of warfare evolves, it is imperative that international norms and regulations keep pace to safeguard humanity and uphold ethical standards in conflict.
Sources
- The shifting battlefield: technology, tactics, and the risk of blurring lines in warfare, ICRC | International Committee of the Red Cross.
- Military use of AI technology needs urgent regulation, UN warns, ABC News.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems